Like humans, businesses operate in an environment that can positively or negatively impact their operations. A business environment is basically the surroundings of businesses. These surroundings are mainly divided into two: micro and macro. The micro environment is also referred to as the internal or inside environment whereas the macro environment is referred to as the external environment.
To be effective, businesses (Small, Medium or Large) will constantly need to analyse both their internal and external environments. To do so, they will need to utilise key strategic tools e.g. SLEPT-D, Value Chain analysis, SWOT etc.
This article will however, focus on one main framework that is widely used to analyse a firm’s internal (micro) environment: the VRIO framework.
The VRIO framework was developed by scholars: Barney and Hesterly in 2006 to help businesses to effectively assess their internal environment with the aim of identifying their core strengths (capabilities) and weaknesses. The framework is rooted in the believe that a firm’s strength and/or core competence is derived from within itself. In other words, the source of a firm’s competitive advantage can be found in the resources it possesses. This is called the resource-based view of strategy.
VRIO is simply an acronym for Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organisation, each of which represents specific sets of questions that must be carefully answered in order to successfully ascertain a firm’s. competitive advantage. The key questions to ask around each are as follows:
1. Value
Are our resources of value to our customers and other key stakeholders? Are we able to effectively and efficiently exploit the resources we have to take advantage of opportunities and/or weaken a competitor?
Note:
a. Resources in this context refers to both your tangible (money, buildings, machineries, fixtures and fittings etc) and intangible (skills, competence etc) resources at your disposal.
b. Value in this context refers to the monetary and social benefits (satisfaction) a customer receives in exchange for the price you offer.
2. Rarity
Are the resources rare or scarce? In other words, is the value you are providing limited in supply? Are you the only business providing that value or do we have few or many businesses doing same? Are you in a monopolistic, oligopolistic or perfectly competitive industry ?
3. Imitability
Can the value you are providing be easily imitated or is it costly to imitate? Imitation here refers to the ease at each a firm’s product or services can easily be copied by others in or outside its industry.
4. Organisation
Do you have the right supporting systems in place to exploit the advantage you have? A good analytical tool to use to ascertain how organised your business is, is the McKinsey 7-s framework. According to McKinsey consultancy, a firm’s competitive advantage is hugely derived from the effective interrelation between the following 7-S’s: Staff, Style (leadership style), Shared-value ( the culture of the business), Systems, Strategy, Skills and Structure.
VRIO and Decision Making
VRIO is thus a great strategic decision making tool in the hands of any business who wishes to effectively compete in their sector and industry. The diagram below shows a synopsis of the different outcomes of a carefully planned VRIO exercise.
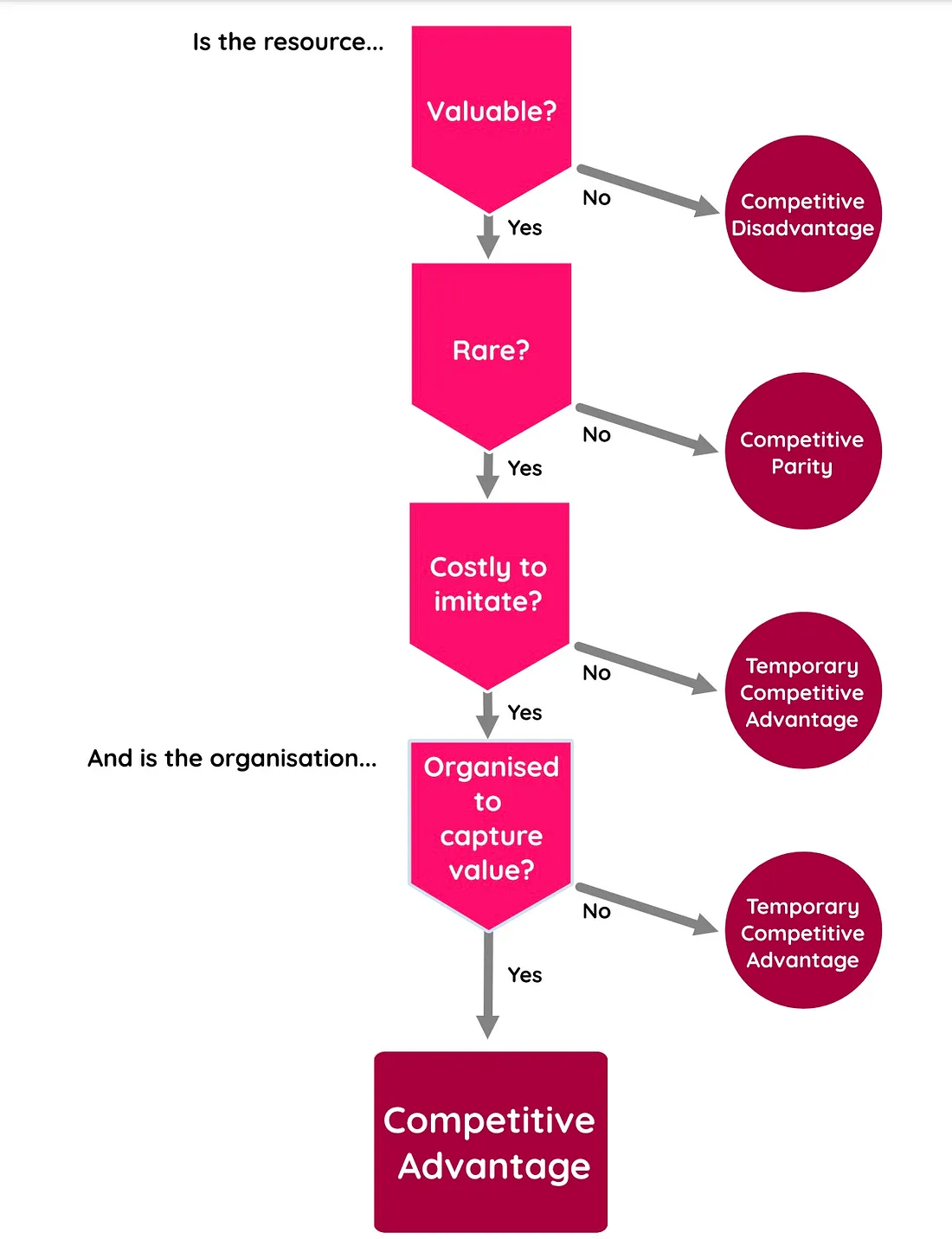
From the diagram above, the following conclusive statements can be made about your firm:
1. If the firm’s resources are not VALUABLE to the market in which its operate, it should be outsourced to a company in another market where that value is needed
2. If the resources are VALUABLE but not RARE, the firm is in a competitively disadvantaged position which simply means that it may not survive in the market space if concrete strategic steps aren’t taken urgently
3. If the resources are both VALUABLE. and RARE but that it is not expensive to imitate or copy, then the firm will have nothing but a competitive parity. It competitors will try to imitate its products in the very near future
4. If the firm’s resources are VALUABLE, RARE and is also very expensive to IMITATE but that it is unable to sufficiently organise itself to sustain its advantage, it will end up having a temporary competitive advantage. This was the case with Motorola whose competitive advantage was short-lived by the emergence of companies like Samsung and Apple
5. Lastly, If the firm has VALUABLE resources that are RARE, costly to IMITATE and has the right ORGANISATIONAL setting that is supported by the effective interrelation of the 7-S described above, it will enjoy a SUSTAINED COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE. This is the sort of advantage that Google, Apple, Microsoft, Paypal, Alibaba etc are enjoying.
To put the framework into perspective, here is an example of a VRIO analysis of Apple Plc
•••
Value: Yes
Apple has a strong brand presence and loyalty and provides products that are well designed and convenient for its customers
Rare: Yes
Unlike other mobile phone manufactures, Apple is the only company that has its own software: the iOS. In addition, the software is seen as one of Apple’s USPs (Unique Selling Prepositions).
Costly to imitate? Yes
Apple’s iOS, closed ecosystem and brand loyalty including its complex manufacturing process and organisation is costly to imitate. Comparatively, other devices from their main competitors, like Samsung, Google, Huawei, HTC, LG etc all run on Google’s Android software.
Organisation: can Apple exploit its resources ? Do they have the capability? Yes
Apple has trained and motivated staff, great systems, the right mix of skills, organic (flexible) organisational structures, excellent strategy, dedicated skilled employees, great style of leadership and an awesome organisational culture (shared value), all working together to sustain its competitive advantage.
In conclusion, SMEs as well as large businesses can adopt the VRIO framework to assess their internal environment. The framework helps in identifying their key resources and capabilities and it will show whether they are Valuable, Rare, Imitable and have the right support system (organisation) to exploit its resources and capabilities.